
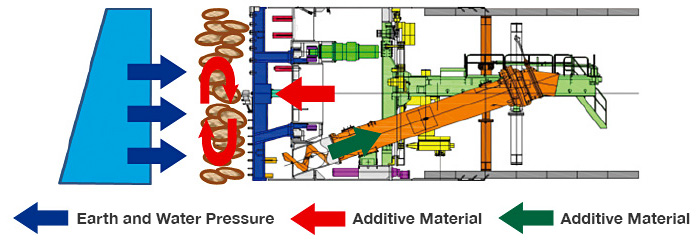
In the Earth Pressure Balance (EPB) shield method, various additives are injected to stabilize the tunnel face by mixing and kneading the excavated soil with the shield cutter to achieve plastic fluidity (muck conditioning), followed by applying the required pressure.
TAC offers a comprehensive range of additives and injection systems—mineral-based, polymer-based, foam-based, and highly responsive composite types—to accommodate all soil conditions.
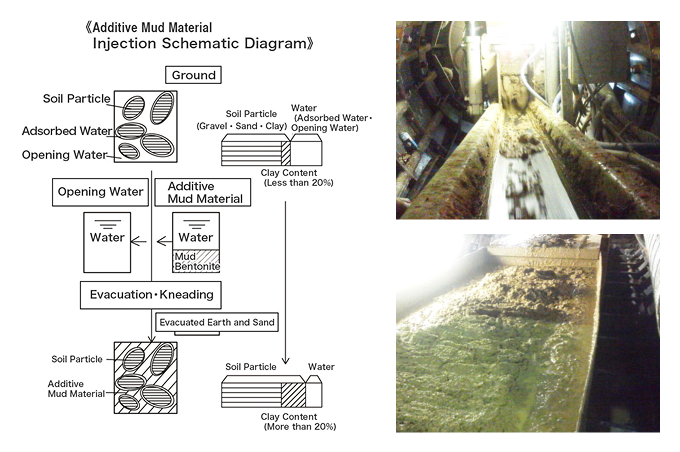
The condition of the excavated soil after Additive Injection is as illustrated in the schematic diagram.
By injecting an appropriate amount of additives, the soil is transformed into a plastically fluidized state, enabling stable and continuous excavation.
Here we introduce the characteristics of excavation additives that can be selected to suit diverse construction conditions and objectives.
| Category | Classification | Product Name | True Specific Gravity (Bulk Density) | pH Value | Main Components | Packaging | Features |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mineral-Based | Clay / Bentonite |
TAC-α TAC-βⅡ TAC-β |
2.6 | 6.9–9.2 (Neutral) | #250 (<63μm), #250 (<63μm), #200 (<75μm) | Bulk, 1t Flexible Container, 25kg Bag | Supplements the fine particles lacking in the ground to be excavated and ensures fluidity of the excavated soil. Serves as the basic material for additive quantity calculations. |
| Surfactant-Based | Foaming Agent | KT-10C | 1.03 | 7.0 (Neutral) | Anionic Synthetic Surfactants | 18kg Can, 200kg Drum, 1t Container | The bearing effect of fine independent foam cells ensures soil fluidity. The dispersing effect of surfactants helps prevent adhesion in clay soils. The air-pressure effect enhances water-sealing performance. |
| Penetrant (Dispersing Agent) | TAC Filter | 0.9 | 8.0–9.0 (Weak Alkaline) | Higher Fatty Acid Salts | 17kg Can | Low-foaming surfactants reduce surface tension on clay surfaces and allow permeation into particles. Highly effective in loosening dense, hard clay soils (with high N-values). | |
| Polymer-Based | Flocculant | TAC Through | 1.06 | 7–8 (Neutral) | Sodium Polyacrylate (Anionic PAM) | 18kg Can, 1t Container | Adsorbs fine particles in excavated soil and aggregates soil and water. Ensures fluidity in sandy soils and prevents excessive liquefaction in clay soils. Forms a coating on clay particles, effectively preventing adhesion. |
| Composite | TAC Carry | (0.8) | 6–8 (Neutral) | Composite Polymer of Super Absorbent Resin (SAP) and Nonionic Thickener (HEC) | 20kg Bag, 500kg Bag | A composite polymer additive developed for soil conveying in gravelly ground. The thickening effect combined with SAP-formed granules provides high fluidity, functioning as a substitute for fine particles in the ground. | |
| Dispersant | TAC Palate | 1.3 | 6–7 (Neutral) | Sodium Polycarboxylate | 20kg Can | Adsorbs onto clay particle surfaces, increasing surface charge and repulsive force. Exhibits steric hindrance to prevent re-adhesion. Reduces injection rates in clayey soils. | |
| Natural Polymer-Based | Thickener | TAC Tector P | (0.3) | 8.5–9.5 (Weak Alkaline) | α-Glucose, Amylopectin | 15kg Bag | A polymer additive made from plant-derived ingredients. Produces high viscosity when dissolved in water. Being naturally derived, it has no environmental impact. |
| Composite | Mineral-Based + Flocculant |
Through Shock | 1.1–1.3 | 10–11 (Alkaline) | Mineral-Based + TAC Through |
Two components are mixed at the tunnel face and used as a highly viscous additive with strong resistance to water dilution. Also used as a backfill material for over-excavation. | |
| Mineral-Based + Plasticity Modifier |
Clay Shock | 1.2–1.3 | 10–11 (Alkaline) | Mineral-Based (TAC-β, βⅡ) + TAC-3G (Plasticity Modifier) |
Two components are mixed at the tunnel face to produce plastic clay. Exhibits excellent shear resistance and forms a plug zone. Widely used to prevent blowout in water-rich gravel layers and as various filling materials. |
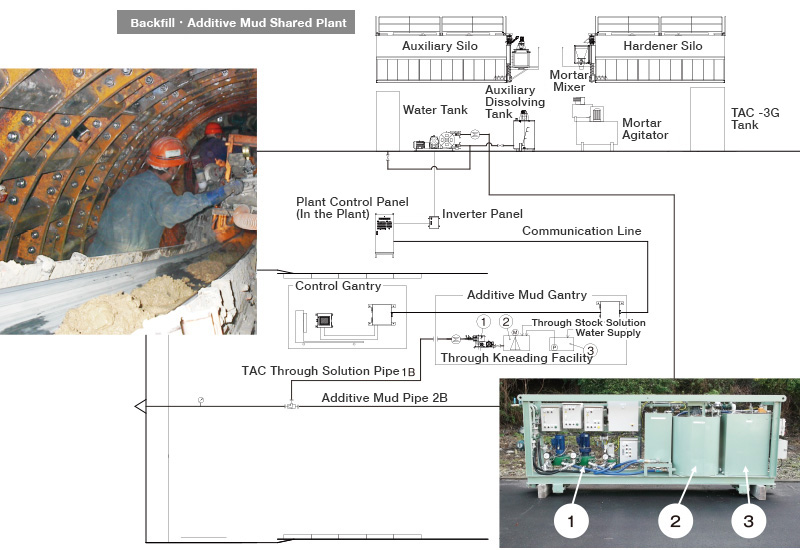
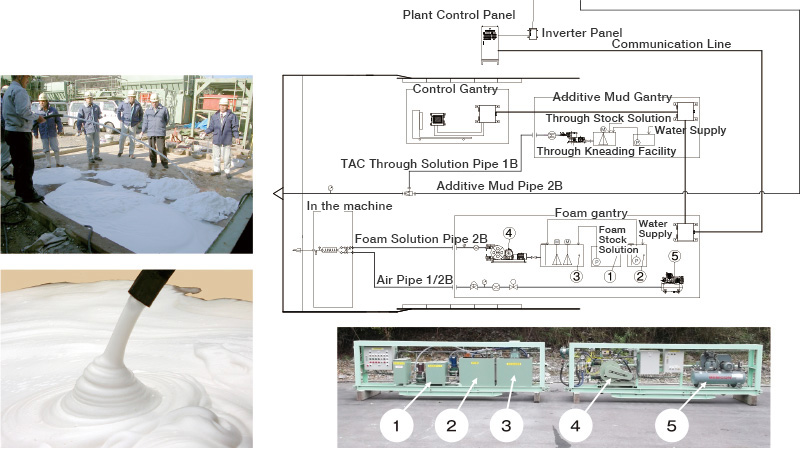
This dedicated injection equipment is designed to supply a wide range of additives accurately and consistently.
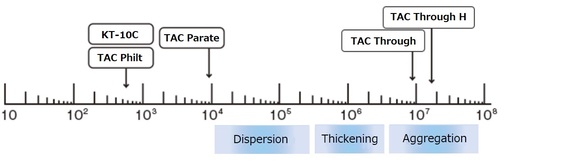
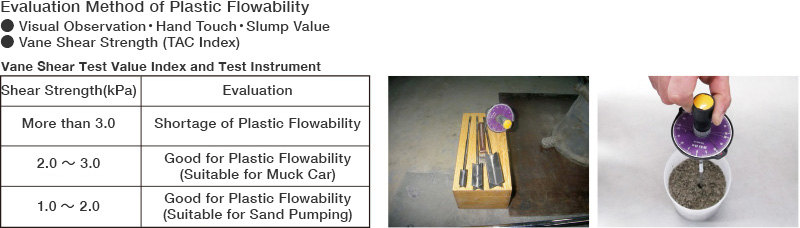
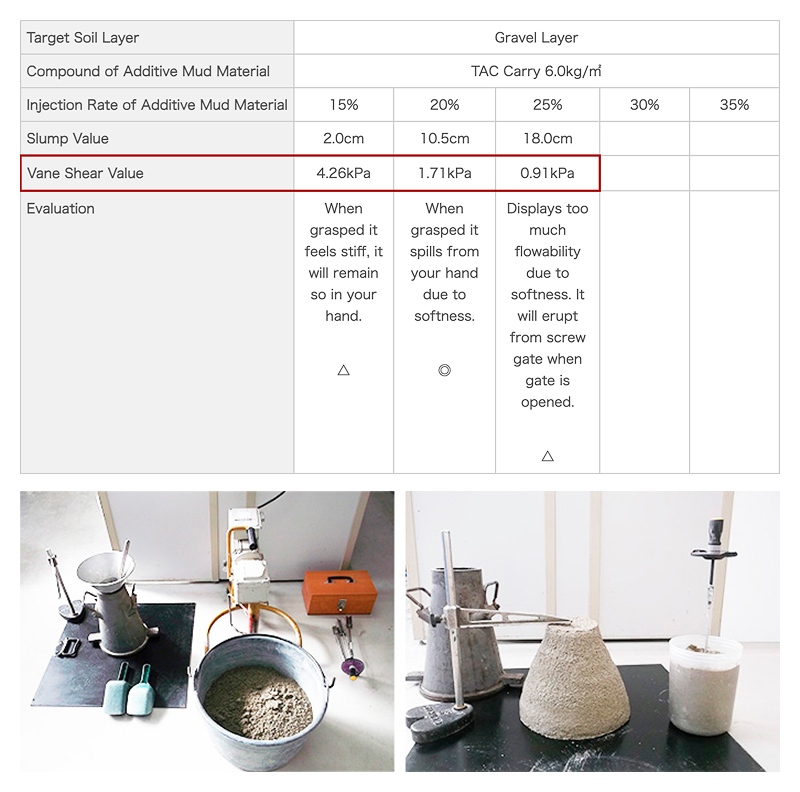
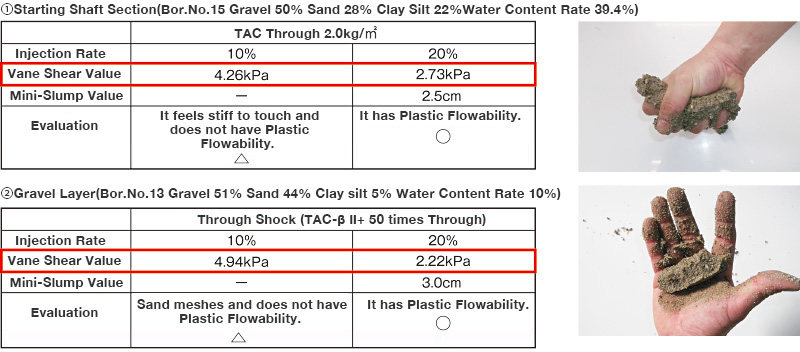
Various tests are conducted to maintain stable excavation performance.
TEL:+81-869-84-2069
Phone Hours::Weekdays 9:00–17:00 (JST)
FAX:+81-869-84-3288